How biomethane is produced
11. 12. 2024
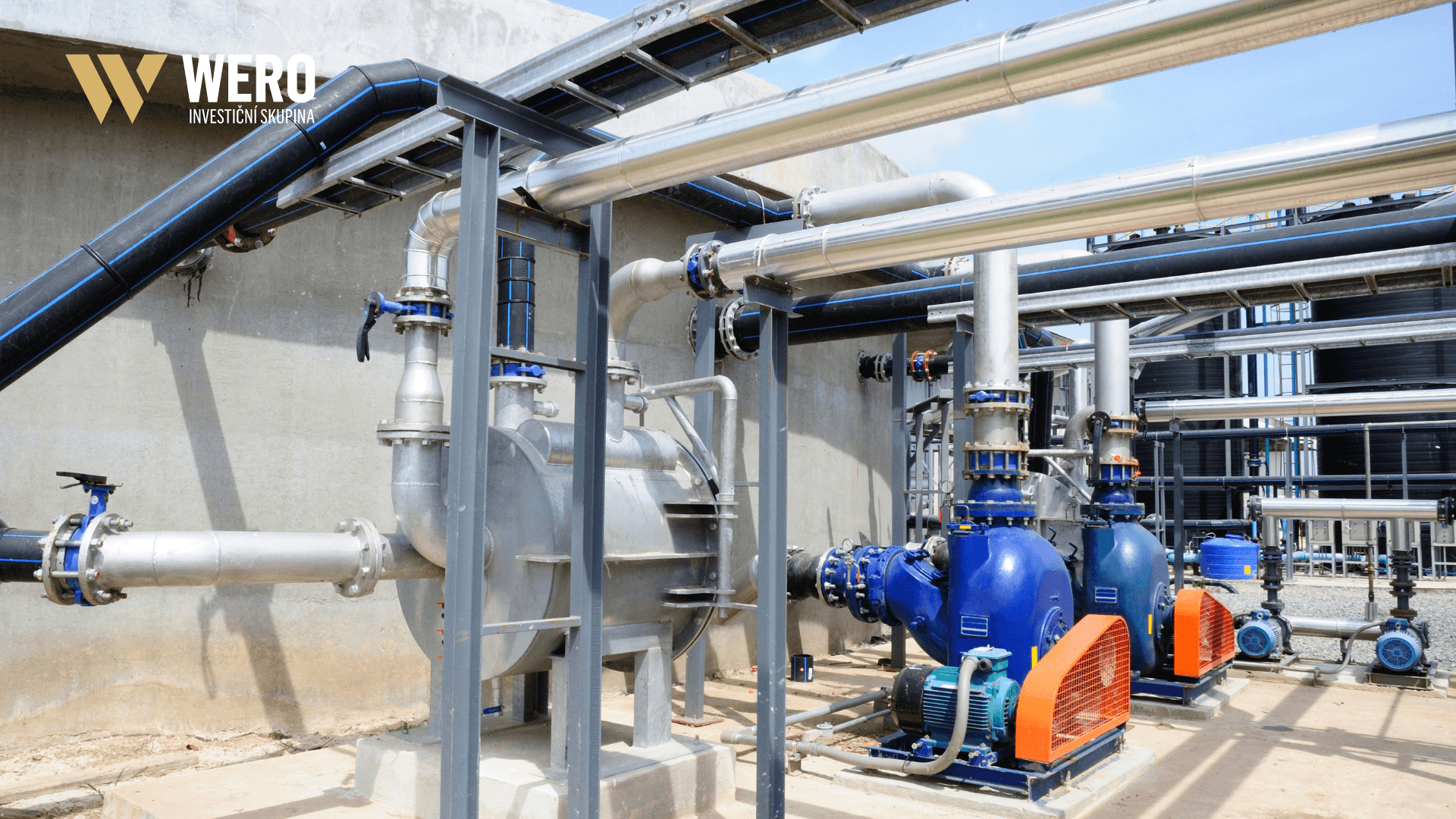
How Biogas Becomes Biomethane: A Key Step Toward Sustainable Energy
Biomethane is a renewable energy source produced by upgrading biogas. Thanks to its properties, it serves as a full-fledged alternative to natural gas and can be used in various applications, from heating and vehicle fuel to electricity generation. This article outlines the process of converting biogas into biomethane and highlights its significance for modern energy systems.
What Are Biogas and Biomethane?
Biogas is created through the anaerobic fermentation of organic materials such as wastewater, agricultural waste, food leftovers, or specially cultivated energy crops. Its composition typically includes:
50–70% methane (CH₄),
30–50% carbon dioxide (CO₂),
Small amounts of other gases like nitrogen, hydrogen, ammonia, and hydrogen sulfide.
Biomethane, in contrast, is highly purified methane (typically over 96% methane content), produced by removing unwanted components from biogas. As a result, it can be injected into existing natural gas infrastructure or used directly as fuel.
The Biomethane Production Process
Converting biogas into biomethane involves several stages:
Raw Biogas Treatment
The first step is removing impurities such as hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), ammonia (NH₃), or dust particles. This phase involves filtering, drying, and sometimes cooling the biogas.
Carbon Dioxide Separation
The primary step is CO₂ removal to increase the methane concentration. Several technologies are used for this purpose, including:
Membrane separation
Water scrubbing
Chemical absorption
Pressure swing adsorption (PSA)
Final Conditioning
After CO₂ separation, the biomethane is further conditioned to meet the required pressure and purity standards for use in gas networks or as compressed natural gas (CNG) for transportation.
Benefits of Biomethane
Environmental Impact
Biomethane is CO₂-neutral, as the carbon it releases during combustion was previously absorbed by plants during their growth.
Waste Utilization
Converting biological waste into energy helps reduce the volume of waste sent to landfills.
Compatibility
Biomethane can be distributed and used in the same way as natural gas, simplifying its adoption.
Importance for Energy Systems
Biomethane plays a crucial role in the transition to more sustainable energy sources. Combined with other renewables like solar and wind energy, it contributes to economic decarbonization and enhances regional energy self-sufficiency.
Conclusion
Biomethane is not only an environmentally friendly solution but also an economically viable one for the future of energy. Continuous advancements in production technology are unlocking new possibilities for its broader application across various sectors. The transformation of biogas into biomethane demonstrates that waste can be a valuable energy resource.
Biomethane is a renewable energy source produced by upgrading biogas. Thanks to its properties, it serves as a full-fledged alternative to natural gas and can be used in various applications, from heating and vehicle fuel to electricity generation. This article outlines the process of converting biogas into biomethane and highlights its significance for modern energy systems.
What Are Biogas and Biomethane?
Biogas is created through the anaerobic fermentation of organic materials such as wastewater, agricultural waste, food leftovers, or specially cultivated energy crops. Its composition typically includes:
50–70% methane (CH₄),
30–50% carbon dioxide (CO₂),
Small amounts of other gases like nitrogen, hydrogen, ammonia, and hydrogen sulfide.
Biomethane, in contrast, is highly purified methane (typically over 96% methane content), produced by removing unwanted components from biogas. As a result, it can be injected into existing natural gas infrastructure or used directly as fuel.
The Biomethane Production Process
Converting biogas into biomethane involves several stages:
Raw Biogas Treatment
The first step is removing impurities such as hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), ammonia (NH₃), or dust particles. This phase involves filtering, drying, and sometimes cooling the biogas.
Carbon Dioxide Separation
The primary step is CO₂ removal to increase the methane concentration. Several technologies are used for this purpose, including:
Membrane separation
Water scrubbing
Chemical absorption
Pressure swing adsorption (PSA)
Final Conditioning
After CO₂ separation, the biomethane is further conditioned to meet the required pressure and purity standards for use in gas networks or as compressed natural gas (CNG) for transportation.
Benefits of Biomethane
Environmental Impact
Biomethane is CO₂-neutral, as the carbon it releases during combustion was previously absorbed by plants during their growth.
Waste Utilization
Converting biological waste into energy helps reduce the volume of waste sent to landfills.
Compatibility
Biomethane can be distributed and used in the same way as natural gas, simplifying its adoption.
Importance for Energy Systems
Biomethane plays a crucial role in the transition to more sustainable energy sources. Combined with other renewables like solar and wind energy, it contributes to economic decarbonization and enhances regional energy self-sufficiency.
Conclusion
Biomethane is not only an environmentally friendly solution but also an economically viable one for the future of energy. Continuous advancements in production technology are unlocking new possibilities for its broader application across various sectors. The transformation of biogas into biomethane demonstrates that waste can be a valuable energy resource.

